
To start a private label company, you need to conduct market research to identify a product niche, source a reliable manufacturer, build a strong brand identity, and establish sales channels.
Step 1: Research and Planning
- Develop a business plan: Define your business goals, target audience, budget, and financial forecasts.
- Conduct market research: Analyze current market trends to identify products with high demand, low competition, and good profit potential. Look for a unique selling proposition that will make your product distinct.
- Define your niche: Choose a product category that you are interested in and can confidently sell, such as cosmetics, supplements, or household items.
Step 2: Product Sourcing and Development
- Find manufacturers: Use online directories such as Alibaba, Thomasnet, or MakersRow to find potential private label manufacturers.
- Vet potential partners: Contact several suppliers and inquire about their pricing, minimum order quantities (MOQ), production timelines, customization capabilities, and quality assurance certifications (e.g., FDA approval).
- Order and test samples: Before committing to a large order, request samples to evaluate the product quality and ensure it meets your expectations and standards.
Step 3: Branding and Legalities
- Create your brand identity: Develop a compelling brand name, logo, packaging, and design that resonates with your target audience. Invest in high-quality packaging and labeling that reflects your brand’s values.
- Establish legal structure: Register your business entity and obtain a business license and tax ID.
- Ensure compliance: Make sure your products comply with all relevant safety standards and regulations.
Step 4: Sales and Marketing
- Set up sales channels: Decide where to sell your products. Common options include your own e-commerce store (using platforms like Shopify), online marketplaces (like Amazon or eBay), or in-person markets.
- Create compelling product listings: Use high-quality images and engaging, keyword-rich product descriptions to attract customers.
- Develop a marketing strategy: Promote your brand using social media marketing, email campaigns, influencer partnerships, and paid advertising to drive traffic and sales.
- Gather feedback: Encourage customer reviews and use feedback to improve your products and processes.
To manage private label inventory, businesses can use a variety of tools and platforms, ranging from e-commerce native solutions to dedicated, feature-rich Inventory Management Systems (IMS) and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS).
E-commerce Platform Integrations
Many private label sellers begin by using the built-in inventory management features of their chosen e-commerce platform, which are often suitable for basic tracking and sales synchronization.
- Shopify: Offers integrated inventory management, multi-location tracking, and low-stock alerts. It is a good option for D2C (Direct-to-Consumer) brands wanting customization and control over their storefront.
- Amazon (FBA): While a sales channel, Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) handles the logistics, storage, picking, and shipping of products. Sellers still need to manage their supply to Amazon’s warehouses, often using Amazon-specific tools or third-party software that integrates with the platform.
- Square for Retail / Lightspeed Retail: These platforms combine Point of Sale (POS) and inventory management, making them ideal for private label businesses that also have a physical store presence.
Dedicated Inventory Management Software
For businesses with high volume, multiple sales channels, or complex supply chains (e.g., managing raw materials for manufacturing), dedicated inventory management software is more appropriate.
- Zoho Inventory: A cloud-based, cost-effective solution ideal for small to mid-sized businesses, offering multi-channel selling integration, real-time tracking, and automated reorder notifications.
- Finale Inventory: Designed for high-volume sellers and Amazon FBA users, it offers detailed tracking (including bin locations), barcode scanning, and automated purchase order generation.
- Ordoro: Known for its automation features, it is a good fit for businesses that use a mixed fulfillment model, including dropshipping, and need to manage purchase orders and shipping easily.
- Katana: Caters specifically to manufacturers and D2C brands that produce their own goods, providing visibility into raw materials, work orders, and production schedules.
- SkuVault: A warehouse-focused system that uses barcode-driven workflows, multi-location logic, and quality control tools to ensure high accuracy in warehouse operations.
Key Features to Consider
When choosing a platform, look for features essential to private label operations:
- Real-time synchronization across all sales channels to prevent overselling or stockouts.
- Automated reordering points and low-stock alerts to streamline replenishment.
- Barcode and QR code scanning support for efficient and accurate stock tracking.
- Integration capabilities with your existing e-commerce platforms, accounting software (like QuickBooks or Xero), and shipping carriers.
- Demand forecasting using sales trends and data analytics to optimize inventory levels and cash flow.
For 2026, the most promising private label niches for marketplaces focus on consumer values like health and wellness, sustainability, personalization, and technology integration.
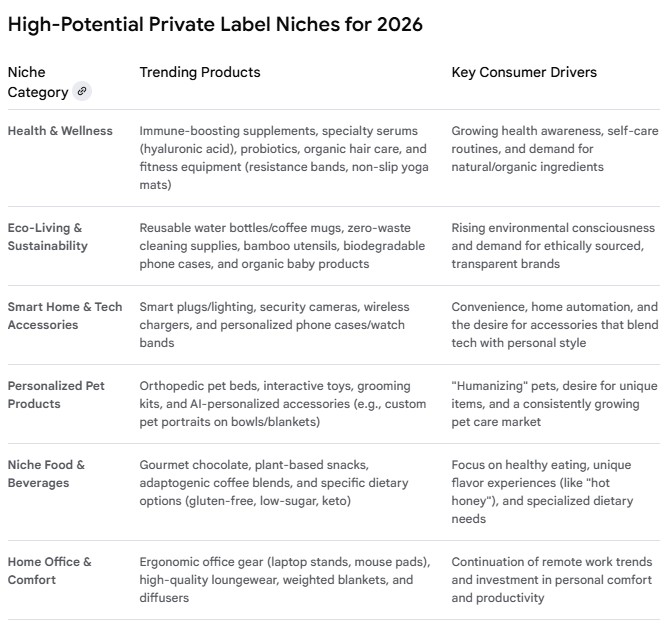
Key Success Factors for 2026
- Focus on Niche Markets: Instead of general “skincare,” target a specific niche like “organic, anti-aging serums for sensitive skin”.
- Emphasize Value & Quality: Modern private label products are no longer seen as “cheap alternatives.” Consumers, including Gen Z, seek high-quality, reliable goods that rival national brands.
- Leverage AI and Personalization: Integrate personalization options (e.g., print-on-demand designs, custom formulations) to make products feel unique to the customer.
- Prioritize Transparent Sourcing: Be open about your product’s origins and manufacturing processes. Highlight third-party certifications (e.g., organic, fair trade) to build consumer trust.
- Capitalize on Passion-Driven Communities: Target consumers who are passionate about specific hobbies like DIY crafting, gaming, or fitness, as they often have high engagement and brand loyalty.
Discover more from Holistic Lifestyle Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

